SEO process basics
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the visibility of a website or a web page in search engines via the "natural" or un-paid ("organic" or "algorithmic") search results. In general, the earlier (or higher ranked on the search results page), and more frequently a site appears in the search results list, the more visitors it will receive from the search engine's users. Source: Wikipedia
There are 8 essential steps, which you can follow to run a successful SEO-campaign:
1. Brainstorm
From the beginning it is very important to choose the relevant keywords or phrases. One of the tactics which many marketeers use is to brainstorm in 3 stages:
- Ask colleagues and friends to help you. Write down all the keywords, phrases that come to mind – focus on quantity. Withhold your criticism, welcome unusual ideas and don't choose.
- Next, use your brains and intuition to refine the keywords. Delete all keywords you think are irrelevant or not suitable for your site and its topics.
- Now you should refine the list further and choose which keywords are you really going to work with (you should probably keep the deleted keywords saved on your computer for later as well).
2. Screening
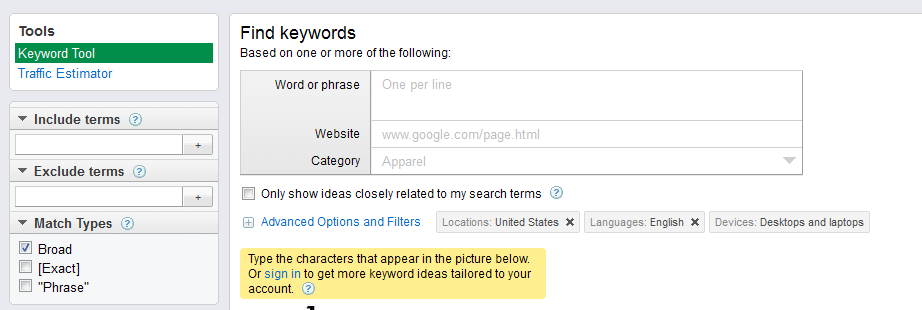
After you finished brainstorming, you should begin with the keywords research. The idea is to screen all the keywords with the help of specialized Keyword tools. Free Google AdWords Keyword Tool is a good choice for this.
You proceed by entering your keywords or phrase one per line setting up your list (don't forget to use the right options: location, language, devises etc.). When finished - click on Search.
Now you'll see a table with the different stats and results for your keywords. The most interesting column is Global Monthly Searches. But if you run a local campaign take a look at Local Monthly Searches. By the way, don't be distracted by the Competition column as it has to do with the paid non-organic searach results for Google AdWords.
Export the sheet to Excel and do some cleaning: delete all irrelevant keywords and information.
Tip: take a look at the keyword suggestions which Google offers for you. There are often some good ideas. (You can find it under the list of your keywords in Google Keyword Tool.)
In Excel create three columns. Keywords, Global or Local Monthly Searches (which you'll have in your downloaded sheet from Google Keyword Tool) and make a new one Search Engine Results.
The third column helps you to check out the competitiveness of your keywords. Working keyword by keyword put them into the Google search one by one and copy/pase the results (see the image below) back into your Excel sheet.
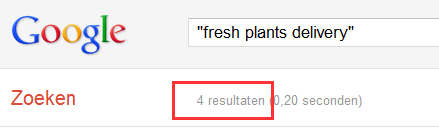
Now you'll have a nice overview of all the keywords and phrases together with the stats and competitiveness numbers.
For analysis purposes you should mainly compare monthly searches with the competitiveness results. For example, if the keywords 'fresh plants delivery' has 50 monthly searches but you get just 4 results by looking it up in Google, this could be an interesting keyword to use. The best ratios depend on the website, its type, topic, goals and audience and should be found out experimentally.
If the amount of monthly searches is low and Search Engine Results number (competitiveness) is quite high, such a keyword would not make a good choice for search engine optimization.
If you run an unique business or have lots of niche information don't be afraid to use your specific keywords too (even if they are not shown in monthly searches). Just try to find a right balance between your keywords and what people are mostly looking on web.
3. Keywords
Now, after the screening you will have a list of keywords which you can use for your meta-information. Don't panic if you have lots of them. You can always use some of them later on. But for general meta-information choose maximum 5-10 keywords or phrases. They should be the most unique and specific to your business.
4. Description
Next comes your meta-description. Using researched keywords write a short and conscious description. It should be no longer than two short sentences. Be creative and don't forget that you should be describing your USP (Unique Selling Proposition) here. See the image below.

5. Implementation
Depending on your system implement your meta-information via a back-end (in case of CMS) or in code. Don't forget to check if the changes are actually applied (by taking a look at the source code in the browser).
6. Copywriting
Now it is time for copywriting. This is, actually, the most crucial part of all SEO. Using your researched keywords and phrases you should write the texts for all your site pages. If the texts have already been written, try to integrate the keywords into them.
It is strongly advised to hire a professional copywriter to write the texts for your site as it will result in content of a much higher quality. But if you have to do it yourself here are some tips:
- Determine the topic of your page
- Determine the most important keywords and use them
- Don't write only for the search engines, write for your visitors
- Provide a logical story
- Your introduction (teaser) has to be 50-100 words maximum.
- Use title tag en headline tags to create a hierarchical semantic structure for your page
- Words highlighting (<em>, <strong>), hyperlinks and anchor text could make a world of difference
7. Optimizing
You probably still have many other pages on your web-site you could optimize. Don't forget unused relevant keywords from your lists and try to have at least a couple of unique keywords on each page important to your business.
8. Fine tuning
This is the last and a very important step of the SEO-process. When you run a SEO-campaign the statistics is of crucial importance to measure your success of failure.
There are many different statistics and analytics tools available. Google Analytics is free and have become de-facto industry standard in SEO.
But measuring and analyzing is not enough. You should act on the information and make the necessary refinements:
- Look carefully through section Keywords in Google Analytics and note which keywords are doing well and which are not. Make your strategic decisions based on your findings
- Repeat the 'screening' step once again
- Change the keywords / descriptions on the site as needed.
And don't forget that SEO is an iterative process. After the fine tuning you should repeat the above steps again after a month or two.


Add new comment